Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter vol 87
2013
CHISINAU,
MOLDOVA
Institute
of Genetics and Physiology of Plants
The genetic of kernel set in one of the maize
hybrids
--Mikhailov, ME
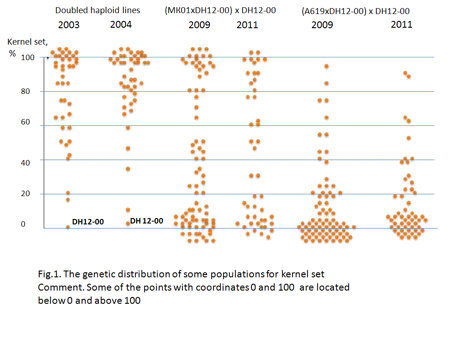
The double haploid
lines derived from MK01 x A619 maize hybrid show the very large spectrum of
kernel set. About 10 lines from 45 are characterized by
full ears (as MK01 parent), 1-2 lines have empty or near empty (few kernels on
ear) cobs, the other lines are intermediate (see Fig.1). This phenomenon is not
due to meiotic aberrations, because artificial pollination produces normal full
ears for all these lines. It appears this is due to difficult outlet of silk
from ear. This feature is clearly inherited from A619 parent line, which shows
the mean kernel set 70-90% at different years (if we take a full ear as 100%). The
hybrid MK01 x A619 is
characterized by full ears, as the parent MK01.
To investigate the
genetic control of this phenomenon, we have chosen the worst double haploid
lines – DH12-00 and derived from it the analyzing crosses
(MK01xDH12-00)
x DH12-00 and (A619xDH12-00)xDH12-00. In 2009 the 79
plants of first cross and the 79 plants of second cross were tested, in 2011
– 47 and 50, respectively. In the first cross the clear bimodal
distribution for kernel set was observed. This suggests the small number of
genetic factors that control this trait and differ in MK01 and DH12-00 lines.
The A619 and DH12-00 lines should be distinguished by larger number of genes.
To evaluate and
eliminate the environmental variation, the selfed
progeny of these crosses were tested (Table 2). The genetic variance obtained
was used for estimation of number of genetic factors influencing kernel set.
Number of factors was estimated by the formula Castle-Wright modified to our
case:
![]() .
.
Mean degree of
dominance β was calculated as
![]()
where KS is mean
kernel set of genotype given in brackets, P is MK01 or A619.
These results,
likely, suggest that variation between double haploid lines for kernel set
caused by two recessive mutation of A619 line preventing outlet of silk from
ear. In the A619 line these mutations do not act in full as they are
compensated by several (5-7) semi dominant suppressors. In a recombinant
progeny this compensatory gene complex breaks down, allowing the full action of
mutation until almost empty ears in some genotypes, including selected for
analyzing crosses the DH12-00 line.
Table 1. Mean kernel
set in 2011
|
Genotype |
Mean kernel set, % |
|
MK01 |
99.8�0.2 |
|
A619 |
82.5�4.5 |
|
MK01xA619 |
99.9�0.1 |
|
DH12-00 |
0.8�0.3 |
|
MK01xDH12-00 |
88.7�3.7 |
|
A619xDH12-00 |
60.4�7.0 |
|
(MK01xDH12-00)xDH12-00 |
39.7�5.6 |
|
[(MK01xDH12-00)xDH12-00] |
33.6�4.6 |
|
(A619xDH12-00)xDH12-00 |
17.9�4.8 |
|
[(A619xDH12-00)xDH12-00] |
11.6�1.7 |
Table 2.
Variances of kernel set and estimation of number of genetic factors
|
Parameter |
[(MK01xDH12-00) x DH12-00] |
[(A619xDH12-00) x DH12-00] |
|
Number of families |
27 |
46 |
|
σ2 between families |
661.58 |
127.65 |
|
σ2 environmental |
58.33 |
22.11 |
|
σ2 genetic |
603.26 |
105.54 |
|
Mean degree of dominance |
0.78 |
0.46 |
|
Number of genetic factors |
2.0�0.6 |
6.0�1.3 |
Please Note: Notes submitted to the Maize Genetics
Cooperation Newsletter may be cited only with consent of authors.