Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter vol 87
2013
Buenos Aires, Argentina.
IEGEBA-CONICET and LACyE (Departamento de Ecolog�a, Gen�tica y
Evoluci�n, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires).
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ZEA KARYOTYPES
Gonz�lez GE*, MF Fourasti�,
C�mara-Hern�ndez J and L Poggio
The taxa of
genus Zea, maize and teosintes, have both intra and interspecific variation in
its genome size, due to differences in heterochromatin
content (Tito et al. Theor. App. Genet. 83:58-64, 1991;
Poggio et al. Ann. J. Bot. 82:115-117, 1998). The
heterochromatin mainly forms telomeric or subtelomeric blocks called knobs (Kato, Mass. Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull. 635: 1-185, 1976).
A comparative analysis
of the karyotypes of different taxa of genus Zea is presented. In
addition, we studied the karyotype variation in the percent and location of
heterochromatic regions, and discuss the inter and intrachromosomal asymmetry for each karyotype.
C and DAPI banding techniques were applied on mitotic metaphases
chromosomes of Zea luxurians
(cv. 2228, Guatemala), Zea mays ssp. mexicana (KG-04-2,
Mesa Central, M�xico), Zea mays ssp. parviglumis (cv.
8391, Balsas Valley, Guerrero, M�xico), Zea
diploperennis (cv. 2232, San Miguel, Jalisco, M�xico) and the
Argentinean race of maize Orgullo Cuarent�n
(VAV 6482, Lab. de Recursos Gen�ticos
Vegetales I. N. Vavilov, Facultad de Agronom�a, UBA).
Chromosomal parameters were measured with MicroMeasure
3.3 (available in http: //www.colostate.edu/depts/biology/micromeasure). Chromosomes
were ordered from the largest to the smallest, as usual for maize, classified
according to the nomenclature of Levan et al. (Hereditas 52:201-220, 1964), in
order to facilitate comparison with related grasses. Intra and interchromosomal asymmetry indexes (A1 and A2) were
calculated according to
Romero-Zarco (Taxon
35:526-530, 1986).
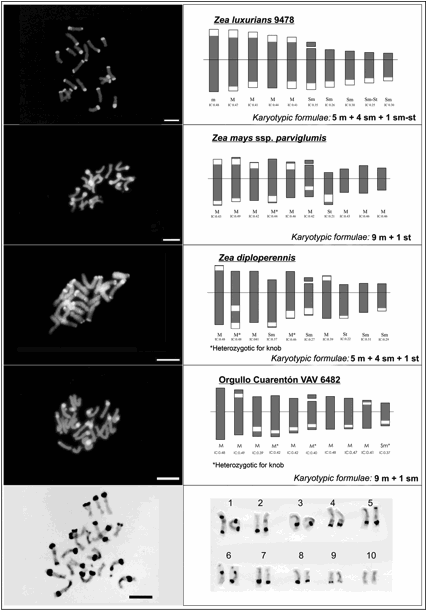
Table 1 present the karyotypic formulae, the intra and interchromosomal
asymmetry indexes, the percent of heterochromatin and the DNA content (2C).
Figure 1 shows the
representative mitotic metaphases, the idiograms and
the karyotypic formulae of each analyzed taxa.
The results of DAPI
banding showed that Z. luxurians is the species with the highest number and
size of heterochromatic knobs, which is related to the higher percent of
heterochromatin and chromosomal size observed in this species. Moreover,
karyotype formulae variation was detected between the studied taxa, mainly due
to the differences in the number and position of the heterochromatic knobs.
In
relation to the symmetry of karyotypes it was noted that Z. diploperennis has the most
asymmetrical karyotype with high levels of intra and interchromosomal
asymmetry, while Z. luxurians
has elevated intrachromosomal asymmetry but low interchromosomal asymmetry. Moreover, Z. m. ssp. mexicana, Z. m.
ssp. parviglumis
and maize Orgullo Cuarent�n
race vary in both asymmetry indices (A1 and A2). This variation is not directly
related with the DNA content or the percent of heterochromatin, but depends on
the heterochromatin distribution. Therefore, the greatest asymmetry observed in
Z. diploperennis
karyotype is due to the heterochromatin distribution mostly on the long arms of
chromosomes.
These results indicate
that in genus Zea, the formulae and
symmetry of the karyotypes depends on the number, size and position of the
heterochromatic regions.
|
|
Karyotype formulae |
A1 |
A2 |
% heterochromatin |
ADN amount (2C) |
|
Z. luxurians |
5m+4sm+1sm-st |
0.39 |
0.15 |
21.16 |
8.83 pg * |
|
Z.m.ssp. parviglumis |
9m+1st |
0.24 |
0.24 |
18.75 |
5.86 pg ◘ |
|
Z.m.ssp. mexicana |
n/d |
0.38 |
0.23 |
n/d |
7.09 pg * |
|
Z.diploperennis |
5m+4sm+1st |
0.44 |
0.37 |
8.5 |
6.36 pg * |
|
Maize (Orgullo Cuarent�n) |
9m+1sm |
0.21 |
0.23 |
7.84 |
6.15 pg # |
Table 1: Formulae and karyotypic parameters. A1: interchromosomal
asymmetry index. A2: intrachromosomal asymmetry
index. Ref.: m: metacentric. sm:
submetracentric. st: subtelocentric. pg: picograms. n/d:
no data. *: From Tito et al. (1991).
◘: Poggio and Guill�n,
personal comunication. #: From Rosato
et al. (1998).
Figure 1:
Mitotic metaphases, idiograms and karyotypic
formulae of each Zea
taxa analyzed. Bar: 10 �m.
Please Note: Notes submitted to the Maize Genetics
Cooperation Newsletter may be cited only with consent of authors.