Maize
Genetics Cooperation Newsletter 80. 2006.
The study of foreign DNA�s association with the main mitochondrial chromosome using isolated mitochondria
--Nepomnyaschih, DV; Dietrich, A; Konstantinov, YM
It
was shown previously (MNL 64:67-68, 1990, EMBO J. 22:1245-1254, 2003; MNL
78:20, 2004) that isolated maize and potato mitochondria can efficiently uptake
extramitochondrial DNA. Little is
known at the moment about the possibility of imported DNA�s association and/or
integration into the main mitochondrial DNA. To study the specificity of association between foreign DNA
imported into isolated mitochondria and mitochondrial DNA, we used different
genetic constructs with or without regions of homology to the main
mitochondrial chromosome. For this
purpose we prepared 4 types of constructs to be used as substrates for DNA
import into mitochondria: (1) the DR-Zm/gfp construct contains regions identical to the
maize mitochondrial genome, (2) the nad2St/gfp construct contains regions with partial
homology to the maize mitochondrial genome and identical to the potato
mitochondrial genome, (3) the pBs-KS construction (a linear form of the plasmid)
has no homology to mitochondrial DNA, (4) the gfp construct (GFP gene fragment with
ca 400 bp size) used in the DR-Zm/gfp and nad2St/gfp constructs has no homology to mitochondrial
DNA.
In this
note, we report some evidence about the association of foreign DNA, which
penetrates into maize mitochondria through the DNA import mechanism with the
main mitochondrial chromosome.
Maize mitochondria were isolated from 4-day-old etiolated seedlings of hybrid VIR42 MV by the standard method of differential centrifugation. The substrate DNA used for mitochondrial import assays were the constructs DR-Zm/gfp, nad2St/gfp, linear pBluescript-KS+ and a fragment of the gfp (Green Fluorescent Protein) gene. To obtain the radioactive linear fragment, 50 ng of unlabeled PCR product and corresponding primers were used for a single PCR cycle in which a 10 min elongation in an unlabeled dCTP-deprived reaction medium containing 100 mCi of [α-32 P] dCTP (3000 Ci/mmole) per 50 ml was followed by the addition of 0.2 mM unlabeled dCTP and a further 5 min elongation. Standard mitochondrial import of DNA was carried out in 40 mM potassium phosphate and 0.4 M sucrose pH 7.0 (import buffer). The samples containing 5-10 ng of 32P-labeled DNA and an amount of purified mitochondria corresponding to 200 μg of proteins were incubated at 25�C for 45 min under mild shaking. Then, mitochondria were pelleted and resuspended in buffer containing 330 mM sucrose, 90 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2 , 12 mM tricine, 5 mM KH2PO4, 1.2 mM EGTA, 2 mM DTT, 2 mM ADP, 10 mM sodium succinate, and 0.15 mM of each dNTP. After incubation at 25�C for 60 min under mild shaking, mitochondria were pelleted and the final pellets were extracted with one volume of 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1% (w/v) SDS pH 7.5 and one volume of phenol. The nucleic acids recovered in the aqueous phase were ethanol-precipitated, fractionated by electrophoresis on a 1% (w/v) agarose gel and transferred onto a nylon membrane (Hybond N+, Amersham Biosciences) for autoradiography.
We showed (Fig. 1) that the existence of species-specific sequences in the DR-Zm/gfp construct is the main requirement for imported DNA to be associated and/or integrated into the main mitochondrial DNA. We need additional evidence now to be sure that foreign sequences associated with the main mitochondrial DNA are integrated into the mitochondrial chromosome.
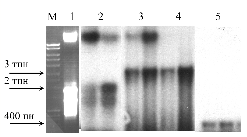
Figure 1. Study of the association of DNA imported into isolated maize
mitochondria with high molecular weight mitochondrial DNA. 1) High molecular weight DNA of non-treated
mitochondria (ethidium bromide staining); 2) the DR-Zm/gfp construct (electrophoresis in denaturation
conditions); 3) the DR-Zm/gfp
construct; 4) the nad2St/gfp construct; 5) the gfp construct.
Financial
support from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grants 05-04-49137 and
05-04-22004-NCNI) is acknowledged.
_________________________________________________
Please
note:
Notes submitted to the Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter may be cited only
with consent of the authors.
Return to MNL 80 on-line index.
Return to MNL index.
Return to MaizeGDB home page
____________________________________________