Maize
Genetics Cooperation Newsletter 80. 2006.
Beijing, China
Institute of Genetics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Effect of space on leaf cell plasmadesma in maize (Zea mays L.)
--Zeng, M; Zeng, Z; Ji, H
In our previous papers, we described a significant influence on progeny of dried maize seeds exposed to a special environment, space. Variation and mutant types of qualitative and quantitative traits were obtained and observed. Effects, both positive and negative, on young plants, ears and kernels were observed. The changes for cell ultrastructure of young leaves have been reported (MNL73:6-10; Chinese Space Sci. Technol. 18(6):63-67). Some changes were observed for plasmadesmata, chloroplasts and mitochondria, in particular thickened plasmadesmata (Figures 1-6).
Plate
Ia Plate
IIb
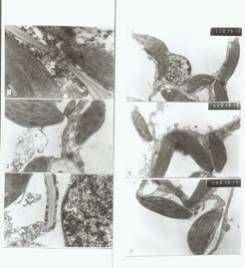
Plate Ia. Figures 1-3 show rich plasmadesmata between cell and cell,
some chloroplasts or chloroplast and mitochondrion around the plasmadesmata,
and swollen plasmadesma. (Fig. 1 X30000;
Fig. 2 X39000; Fig. 3 X30000)
Plate Ⅱb. Figures
4-6 show rich plasmadesmata between cell and cell, some chloroplasts or
chloroplast and mitochondrion around the plasmadesmata. (Fig. 4 X4950; Fig. 5 X4950; Fig. 6
X4950)
According to our observations, we believe that space treatment of dried seed might cause an increase in the thickness of the plasmadesmata, and cause material to be exchanged between cells, further improving the level of metabolism.
_________________________________________________
Please
note:
Notes submitted to the Maize Genetics Cooperation Newsletter may be cited only
with consent of the authors.
Return to MNL 80 on-line index.
Return to MNL index.
Return to MaizeGDB home page
____________________________________________